Configuration
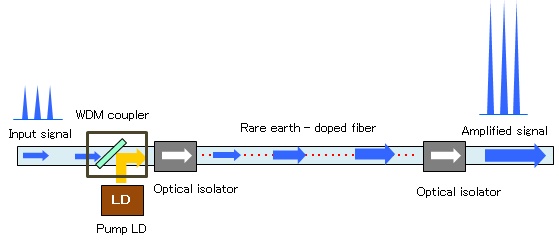
A schematic of a rare-earth-doped fiber amplifier is shown in Figure 1. The input signal is combined with the pump light by the WDM coupler, and is amplified by the pump light via stimulated emission in the rare-earth-doped fiber. Optical isolators are placed both at the input and output, in order to stabilize signal amplification by eliminating unwanted back reflection from the output port, as well as to prevent the amplifier from operating as a fiber laser.
Emission wavelengths from rare-earth elements
Figure 2 shows energy diagrams of various rare-earth elements, showing both pump and emission wavelengths. A rare-earth element absorbs pump light and is raised to an excited level (shown as an upward arrow), and eventually drops to a lower level by emitting light (shown as a downward arrow).
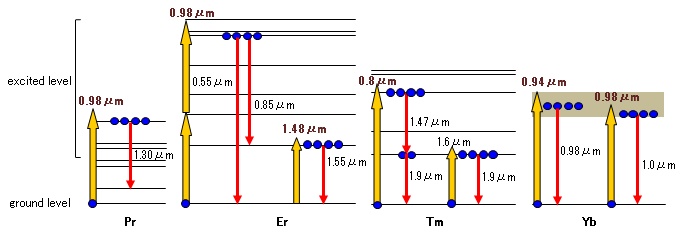
Erbium (Er) shows strong fluorescence in the C-band and L-band and thus erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) is the most common optical fiber amplifier in optical communication. Other common rare-earth elements are Ytterbium (Yb) and Thulium (Tm). Ytterbium and thulium shows strong fluorescence around 1 micron and 1.9 micron, and these two rare-earth elements are commonly used for high-power fiber lasers for non-telecom applications (laser marking, welding, etc.).
In general one photon absorption results in one photon emission, however this is not always the case. One case is called cascaded emission, where one absorbed photon produces two (or more) photons; an example is shown in the energy diagram of Tm. Another case is called upconversion emission, where two (or more) absorbed photons produce one photon; an example is shown in the energy diagram of Er.